Explain Differences Between Packet Segment Datagram
For prior knowledge the Internet which we use is actually based on a Datagram network connection-less at the network. In this article we are going to discuss about two terms frequently used in networking as a unit of data ie frame and packetThe crucial difference between frame and packet is that frame is the serial collection of bits and it encapsulates packets whereas packets are the fragmented form of data and it encapsulates segment.

Difference Between Segments Packets And Frames Geeksforgeeks
In CD collisions are detected as they occur.
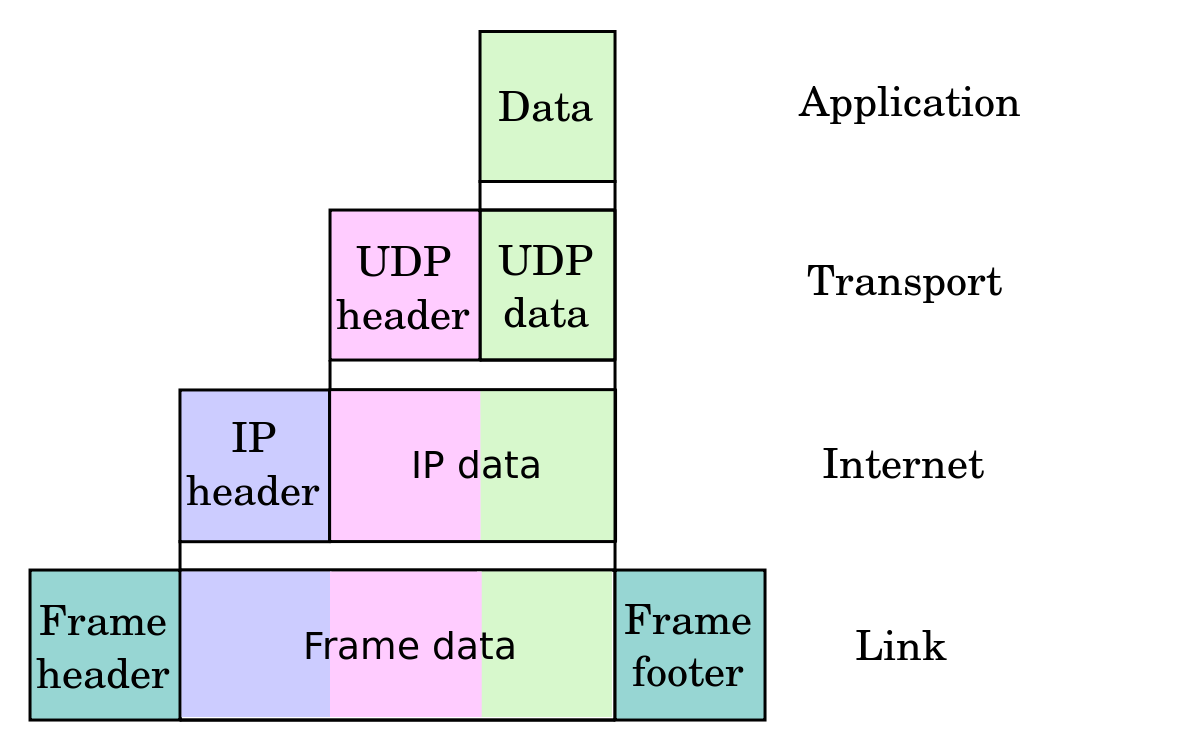
. Some sources do explain that packet is the pdu of the network layer and in most cases it does mean the Network layer pdu used more often than the word datagram. The application data receives a transport protocol header UDP or TCP generally and become a segment. To give a clear picture-.
It is a small transport layer designed on top of IP. The delivery arrival time and order of arrival of datagrams need not be guaranteed by the network. It is a mechanism used for transmitting datagram packets over network.
We noted that network layer functionality can be broadly divided into data plane functionality and control plane functionality. The term packet refers to the data unit of somewhere between the Network and the Link layer. If the transport protocol is TCP the unit of data sent from TCP to network layer is called Segment.
Instead it just describes a well formed message originated by one of the layers. It is the responsibility of H2 to reorder the packets in order to retrieve the original message. The data at this layer-4 is known as segment.
The PDU has a different meaning in different layers still we can use it as a common term. If the network protocol is IP the unit of data is called Datagram. Differences between Virtual Circuits and Datagram Networks.
A PDU Protocol Data Unit is defined by which layer it is in. We say TCP segment is the protocol data unit which consists a TCP header and an application data piece packet which comes from the upper Application Layer. Its natural that it is ambiguous to you.
The PDU of the Data-Link Layer is called Frames. There is no ordering of messages no tracking connections etc. The difference between a router and a link-layer switch is that a router forwards the packet based on the packets IP address and a link-layer switch forwards a packet based on its MAC address.
Back to the question. Each packet is assigned with unique sequence number. Transport layer data is generally named as segment and network layer data unit is named as datagram but when we use UDP as transport layer protocol we dont say UDP segment instead we say UDP datagram.
At transport layer if protocol is UDP we use datagram there as well. The packets in the message arrives in the destination out of order. Explain the difference between a PDU and a datagram.
The IP header consists of source IP address Destination IP address protocol field etc. A datagram is basically an information but there is no guarantee of its content arrival or arrival time. A packet is a block of data with length that can vary between successive packets ranging from 7 to 65542 bytes including the packet header.
The segment receives an IP header and is now a packet. Java DatagramSocket class represents a connection-less socket for sending and receiving datagram packets. TCP is heavy-weight.
As you can see. From this answer on Stack Overflow. A datagram is a basic transfer unit associated with a packet-switched network.
The segments are appended with IP header of size 20 bytes to 60 bytes. Datagram is used in conectionless nw eg. Senders do not signal their intent to transmit but simply start transmitting if they sense no other ongoing transmission.
Packetized data are transmitted via frames which are fixed-length data blocks. TCP requires three packets to set up a socket connection before any user data can be sent. Difference Between Segments Packets and Frames Submitted by Sarath Pillai on Sat 06032017 - 1519 The terms Segment Packet Datagram Frames etc are so much used and reused in different books and articles to convey different meanings that it has now become totally confusing.
A packet is the Internet layer datagram. The layer-2 adds header and trailer to layer-3 data. Datagrams provide a connectionless communication service across a packet-switched network.
Computer networks that provide connection-oriented services are called Virtual Circuits while those providing connection-less services are called Datagram networks. This is used in 2 layers. Hence we differentiate them as UDP Datagram IP Datagram.
What is the difference between datagram and packet. The datagram itself does not have the connotation of any particular layer. Datagrams are typically structured in header and payload sections.
UDP Whereas packets used in connection oriented nw eg. The frame is the network access layer datagram. In other words frame is an L2 datagram packet is an L3 datagram segment is an L4 datagram.
The PDU of Transport Layer is called as a Segment. The PDU of Network Layer is called as a Packet. The four datagram packets labelled as A B C and D all belonging to same message are being routed separately via separate routes.
The transport layer datagram is a segment. The size of a frame including frame header and control information can range up to 2048 bytes. This is the basic meaning of different terms used in Computer Networks.
TCP handles reliability and congestion control. Explain the differences among each group of terms and give illustrative examples whenever possible You can use google search engine to help you find the answers a LAN and WAN b Extranet Intranet Internet with uppercase I and internet with lowercase i c Connection-oriented and Connectionless service d Segment Datagram. Explain the difference between CSMACD and CSMACA.
Give two reasons that IEEE 80211 does not adopt CSMACD. The data at this layer-3 is known as packet. In CA collisions are avoided because each node signals its.
In the physical layer and.
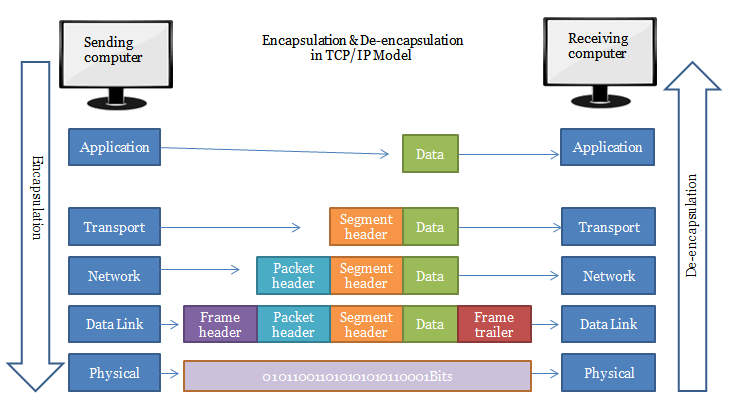
Segments Packets Datagram Frame Cell Bits Differences
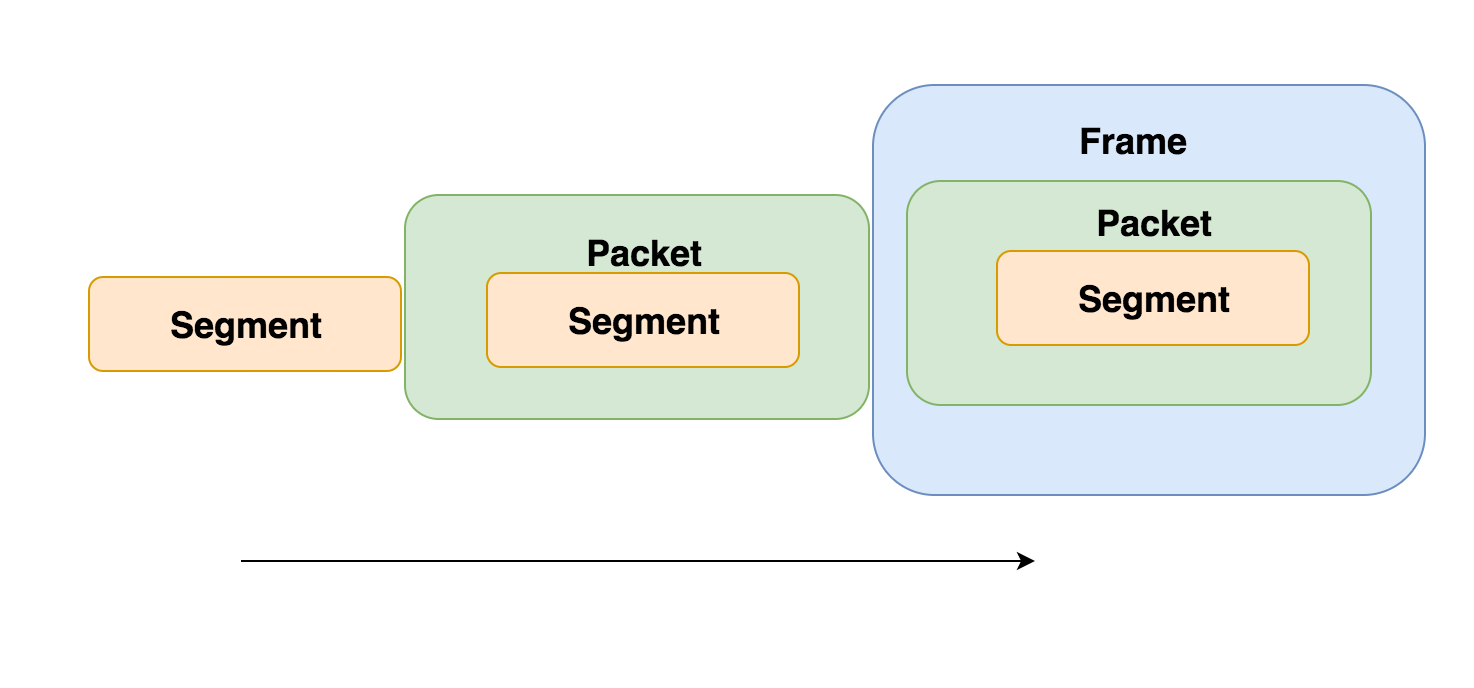
Comments
Post a Comment